Introduction
Olverembatinib (HQP1351), a third-generation BCR-ABL1 inhibitor, has been rationally developed to treat patients with CML that is refractory to or intolerant of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), including acquired drug-resistant mutations. HQP1351 is effective against a broad spectrum of BCR-ABL1 mutations, including T315I, which confers resistance against all first- and second-generation TKIs. A phase I dose escalation study (SJ-0002) was conducted in Chinese patients with TKI-resistant/refractory CML. A total of 101 patients with CML, including 87 with chronic-phase CML (CML-CP) and 14 with accelerated-phase CML (CML-AP) have been enrolled in 11 dose escalation/expansion cohorts ranging from 1 mg to 60 mg HQP1351 every other day (QOD). The maximum tolerated dose (MTD) has been established as 50 mg, and the recommended phase II dose (RP2D) as 40 mg, QOD. To support selection of RP2D, we performed population pharmacokinetic (PK), exposure-efficacy, and exposure-safety analyses based on data from clinical study SJ-0002.
Methods
The population PK analysis was performed on the plasma drug concentration data from 65 patients. Exposure-efficacy analysis was performed on the primary clinical endpoint: major cytogenetic response (MCyR) at 6 months in 89 patients with CML. These included 78 individuals with CML-CP and 11 with CML-AP. Using a cell-life-span model in 101 patients with CML, we also performed an exposure-safety analysis on the most frequent adverse event: reduction in platelet count.
Results
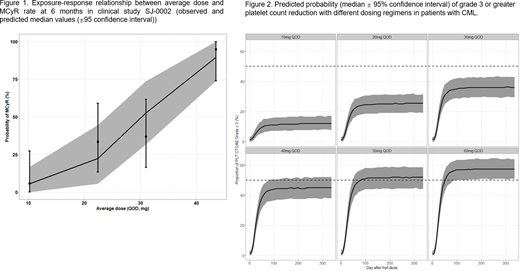
Population PK analysis demonstrated that HQP1351 PK was best described by a two-compartment model with first-order absorption and first-order elimination. Total bilirubin, aspartate aminotransferase, and albumin were found to be significant covariates affecting the PK of HQP1351. In the exposure-response analyses, average dose was selected as the exposure measurement over average concentration at steady state (Cavg,ss) and average trough concentration at steady state (Ctrough,ss) based on the model performance. Exposure-efficacy analysis showed a clear E-R relationship, with the increased probability of achieving MCyR at 6 months with increasing average HQP1351 dose (Figure 1). The highest MCyR rate with HQP1351 was achieved at the MTD (50 mg QOD). In the exposure-safety analysis, there was a significant dose response relationship between average HQP1351 dose and incidence rate of grade 3 or greater (G3⁺) platelet count reductions (Figure 2).
Conclusions
E-R analyses of HQP1351 in Chinese patients with CML demonstrated a clear positive relationship between average HQP1351 dose and both efficacy and the probability of G3⁺ platelet count reductions. The results of E-R modeling and simulation support the RP2D of 40 mg QOD because it achieved a high rate of MCyR with manageable risk of G3⁺ platelet count reductions.
Lu:Ascentage Pharma Group: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Wang:Ascentage Pharma Group: Current Employment. Xu:Ascentage Pharma Group: Current Employment. Men:Ascentage Pharma Group: Current Employment. Xie:Ascentage Pharma Group: Current Employment. Chen:Ascentage Pharma Group: Current Employment. Niu:Ascentage Pharma Group: Current Employment. Yang:Ascentage Pharma (SuZhou) Co., Ltd: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Other: Leadership and other ownership interests. Zhai:Ascentage Pharma (SuZhou) Co., Ltd: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Other: Leadership and other ownership interests.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.